How Imperial Japan used the Shinto holy book ‘Nihon Shoki’ to justify colonizing Korea: a look at Koiso’s 1944 anti-Chinese, anti-American, anti-Communist youth rally
2025-01-13
16
1905
During his reign as Governor-General of Korea from 1942 to 1944, Koiso, a man marked by vanity and a messianic belief in his own vision, sought to do what he believed no other Governor-General before him could achieve: persuade Koreans to abandon their identity and fully embrace being “Japanese.” But Koiso’s approach was unlike his predecessors’. While others sought to forcibly assimilate Koreans by turning them into Japanese, Koiso’s so-called insight was far more insidious—he declared that Koreans were already Japanese and simply didn’t realize it yet. His self-appointed mission? To awaken the “Japanese person” within every Korean.
Koiso’s strategy centered on a mix of religious revival, forced education, and the enforcement of Shinto religious practices. He believed that Koreans would rediscover their “true selves” by observing Shinto rituals and studying Japanese scriptures, particularly the Nihon Shoki. According to Koiso, Koreans’ ancient ancestors were Japanese, and reconnecting with these roots would allow them to transcend their current identity and unify with the Japanese nation. This twisted vision was what he referred to as “being penetrated in the essence of the National Body (国体本義の透徹),” an idea propagated by Koiso’s favorite Kokugaku scholar and Shinto spiritual leader Master Imaizumi (see related 1942 articles about Imaizumi).
To achieve this, with the help of Director Takeuchi (see related Feb. 1943 article about Takeuchi), Koiso established a vast network of training centers aimed at indoctrinating Koreans with Japanese ideology and customs. He also oversaw the construction of Shinto shrines across Korea, often built using forced labor. These shrines were intended to enforce the worship of Japanese deities as a way of spiritually binding Koreans to Japan. After Korea’s independence, these shrines—symbols of cultural oppression—were burned to the ground.
About a month after delivering this January 1944 speech, Koiso would deliver a speech in February 1944 (see related Feb. 1944 article) pointing to a passage in the Nihon Shoki that he claimed proved Koreans’ ancestral ties to Japan. He fixated on the story of Susanoo, the younger brother of Amaterasu, the Japanese sun goddess, who was said to have descended upon a place called Soshimori. Koiso declared this as evidence that Koreans were part of the divine lineage of Japan. The Keijo Nippo newspaper, acting as a propaganda tool, amplified his speech, highlighting key phrases for emphasis. These bolded sections were drilled into Koreans by teachers, patriotic groups, and employers, forcing them to internalize Koiso’s distorted narrative.
Koiso’s vision was not just a form of cultural erasure—it was a deeply arrogant and delusional project to rewrite history itself. His attempt to impose Shinto worship and a fabricated Japanese identity on Koreans was not just oppressive; it was a direct attack on the dignity and spirit of the Korean people.
[Translation]
Gyeongseong Ilbo (Keijo Nippo) January 16, 1944
Japanese and Koreans Share the Same Ancestry and Roots
The Origins of Korean History are Found in the Nihon Shoki
Governor-General Speaks to Drafted Students for the Third Time
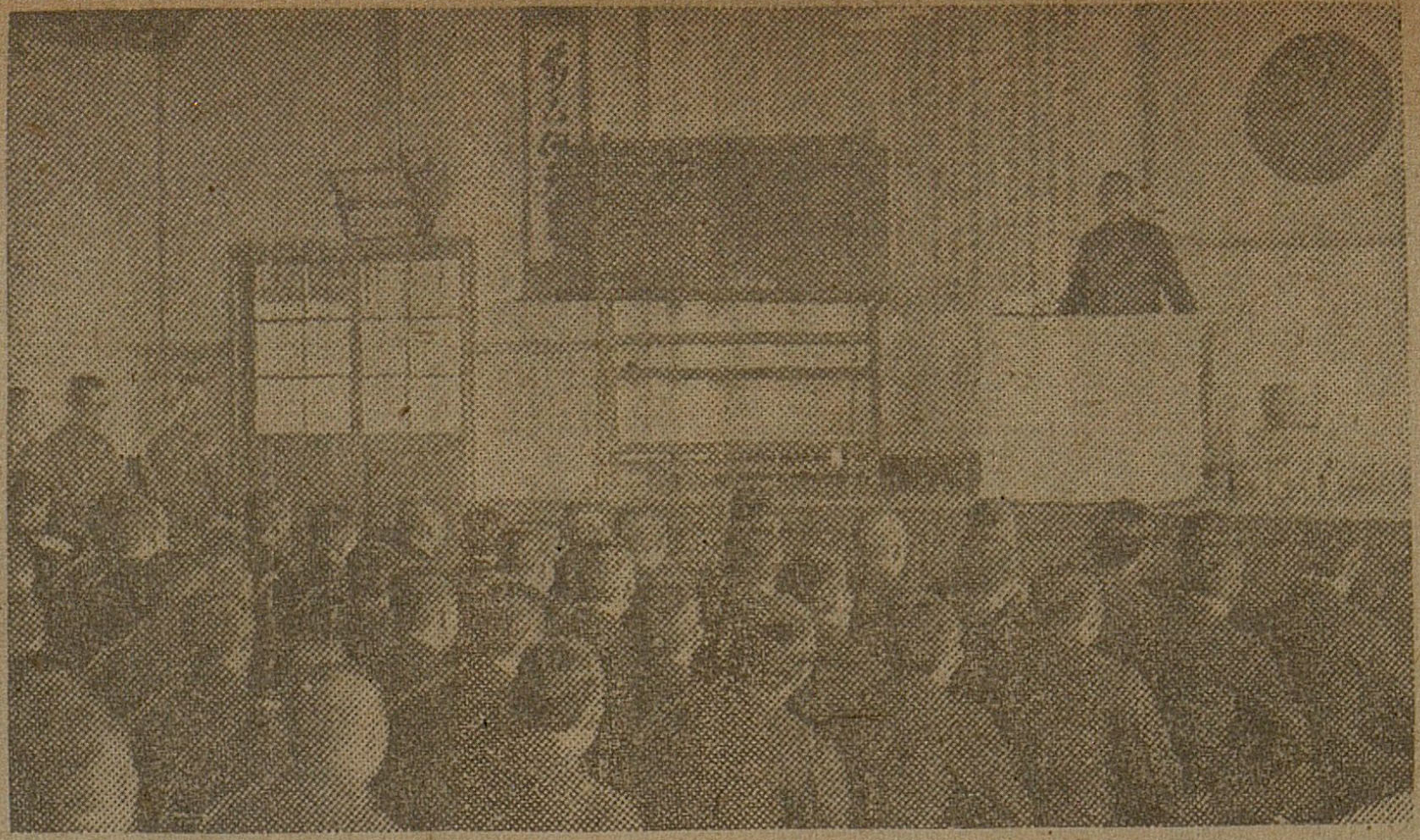
On January 13th, Governor-General Koiso delivered a lecture to the principals of private middle schools who were attending the Leadership Training Institute of the Yongsan Governor-General’s Office. On January 14th, he addressed the elementary school principals who were attending the Educational Research Institute in Samcheong-dong. Accompanied by Secretary Kobayashi and Training Section Chief Takeuchi, Koiso traveled a considerable distance to arrive at the First Volunteer Soldier Training Center in Nohae-myeon (노해면, 蘆海面), Yangju County, at 3:30 PM on January 15th.
There, he once again addressed the second group of drafted students, who had enthusiastically responded to the conscription summons. With a familiar and gentle demeanor, he elaborated on the theory of ‘Japanese and Koreans sharing the same ancestry and roots,’ drawing upon classical texts, and emphasized that they needed to be penetrated by the essence of the National Body. As the third year of the decisive war began, the Governor-General’s continuous efforts over these three days to convey a grand vision and underscore the need to be penetrated by the essence of the national body demonstrated nothing less than his profound determination to stand at the forefront of enlightening the 25 million people of the Korean Peninsula. [Photo = The Governor-General giving a speech to the drafted students]
“The volunteer students have now taken their first step through the gates of this facility. However, reflecting on the fact that some of you did not initially choose to volunteer, I must admit that there were shortcomings on my part. Volunteering, by its nature, allows for freedom of choice in theory. Yet, in the context of this Holy War, which seeks to liberate Asia from Anglo-American exploitation and enable each nation to find its rightful place, there is no room for theoretical reasoning or abstract arguments. We must drive the Anglo-American forces out of Asia entirely! It is with this conviction that I used strong words to inspire you to rise to the occasion,” Koiso stated.
Koiso went on, ‘While various circumstances may have contributed to the presence of those who did not volunteer, I feel that, as someone entrusted with the governance of Korea, my leadership and example have been insufficient. For young men, especially, strong and vigorous training is necessary, as is an environment filled with warmth and camaraderie. It was with this in mind that I brought you here to this training facility. Once your training is complete, your peers will be striving to navigate these difficult times, and I believe it is an act of kindness on my part, from my position, to guide you toward fulfilling the vital responsibilities of war. This conscription is not just for your benefit but also to take the lead in Korea’s industrial development. By stepping forward as industrial warriors, I hope you will proudly and confidently pave the way for the nation’s progress. Here I will share with you some of my sentiments that I believe you will need.“
With these words, he framed the discussion of Korea’s governance policies, explaining the trajectory of the administration of Korea up to the present day. Each sentence of the Governor-General’s remarks calmed and steadied the spirits of the students, who had just concluded their entrance ceremony. He first highlighted the emergence of a fervent spirit of patriotism that had begun to rise across the peninsula around the end of last year.
It was stated that the governance of the Korean Peninsula up to the present day had been hindered by Chinese thought, Anglo-American thought, and finally, Communism. “Chinese thought replaced the corrupt Buddhism of the Goryeo era when the Joseon dynasty adopted Confucianism as its primary ideology. In their excessive admiration for all Chinese ideas, they obstructed Japanese governance. Next came Anglo-American thought in the form of Christianity, which was nothing more than an attempt to impose Anglo-American concepts of logic and morality. Behind it lay ambitions for exploitation, which found Japan’s principle of universal equality distasteful. Following this was Communism,” he explained.
He asserted that, while people in areas such as mainland Japan, Manchuria, and Northern China criticize the Korean people, their criticism does not do justice to the true essence of the Korean people. Rather, such criticisms stem from the lifestyle shaped over the 500 years of the Joseon dynasty. The true essence of the Korean people must be sought far back, tracing the origins of the Korean ethnic group, and this origin, it was clearly pointed out, is found in the Nihon Shoki. Before the students who listened intently, the theory of ‘Japan and Korea sharing the same ancestry and roots’ was presented with a powerful argument.
“If anyone were to oppose this view, they would be opposing what is clearly and explicitly written in the Nihon Shoki. Upon examining the true essence of the Korean people, it is evident that Japanese and Koreans share the same ancestry and roots. Although we have had to use the term ‘Japanese-Korean Unification’ lately, this was due to a lack of thorough investigation. We must strive to understand the culture brought forth by this shared heritage and grasp the essence of the National Body.
In doing so, we must consider what kind of spiritual and cultural framework our shared ancestors possessed. To truly understand the essence of the National Body, we must remember and reflect upon the principles laid out in the Three Divine Instructions: the Clarification of the National Body (Kokutai Meichō), the Sacred Mirror and Sacred Rice Ear (Saikyō Saiho), and the Divine Mirror and Eternal Boundary (Shinkyō Bankyō).“
The Governor-General proceeded to explain the profound philosophy of the Three Divine Instructions in a way that was easy to understand. The listening students, now in a state of serene attentiveness, etched each word deeply into their minds. He then continued, expounding on the spiritual principles contained within the philosophy of the Eight Deities’ Shrine and encouraging the students to thoroughly study the Three Divine Instructions. He gently advised them, saying, “By fully mastering these teachings, you will be able to purge the harmful influences of the five centuries of Confucianism propagated during the Joseon dynasty, which have taken root in your spirits.“
The Governor-General remarked, “If I had been able to convey these thoughts more earnestly and clearly a little earlier, I believe I could have guided you to an even happier state today.” For this reason, on the previous night, and the night before that, he worked late into the night, passionately addressing those involved in education. He called for a thorough penetration by the essence of the National Body, which is rooted in the grand spiritual and cultural framework woven since the age of the gods, and fervently advocated for the establishment of a Righteous Korea.
Finally, he stated, “Let us set aside all past matters and face the present. Born as men, we must clearly grasp the ideals of the spirit. To live a life of indulgence without purpose is to render one’s existence meaningless. The meaning of life lies in fully being penetrated in the essence of the National Body and uniting with the ancestors who bequeathed this magnificent philosophy.“
He added, “If the opportunity arises, I hope to visit you once again during your training and engage with you further. I believe you understand the aspirations I have for you—do you?” With a warm smile, he asked this of the students, to which they responded with a powerful “Yes!” Their enthusiastic reply resounded, marking the end of the Governor-General’s two-hour-long address, after which he shared a meal with the trainees and departed the training facility at 6 PM.
[Transcription]
京城日報 1944年1月16日
内鮮は同祖同根
半島史の根源は『書紀』
総督、三度び徴用学徒に説く
十三日には龍山総督府指導者錬成所に入所中の私立中等学校長、十四日は三清町教学研修所に入所中の国民学校長にそれぞれ訓話を行った小磯総督は小林秘書官、竹内錬成課長を伴い十五日午後三時半長駆、楊州郡蘆海面の第一志願兵訓練所に来所。同日徴用のお召しに感激して馳せ参じた第二次徴用学徒に再び諄々と馴染み深い優しい面持で古典に則り内鮮同祖同根論を説き、国体本義の透徹を強調した。決戦三年が明けてこの三日間ぶっ続けで遠大な論旨をもち国体本義の透徹を説く総督はとりもなおさず半島二千五百万教化の陳頭に立つ至大な決意の現れでもあった。【写真=徴用学徒に説く総督】
『いまや志願学徒は営門の中に第一歩を印することとなったが、諸子は志願するに至らなかったことに関し、一面観察するに、自分の至らなかった点もあると思う。志願なのであるから理論としては選択の自由が保留されているとも思われるが、米英の搾取から亜細亜を解放し、各民族をして各々そのところを得せしめる今次聖戦下にあっては一切の理窟、理論を抜きにして米英の勢力を亜細亜から駆逐しなければならないのであって、かく考えたればこそ小磯は強い言葉をもって諸子の奮起を促したのである。
諸種の環境から然らしむるとは謂え未志願者を出したこと、小磯乏しきながら朝鮮統理に任じ指導垂範の足らざるところがあったと思う。男子として特に若い青年として強健なる鍛錬も必要であり、人情たっぷりな雰囲気が必要と思い、諸子を本訓練所に入ってもらった。訓練を終えれば同僚が時局を乗り切るために努力するのであるから、諸子を戦争の要務に導くということがこれ小磯の立場から諸子にしむける親切心であろうと思って、ここに集まってもらった。徴用は諸子のためばかりではなく、半島の立地条件に伴い換言すれば朝鮮の産業的に立上らんとする勤務者の先陣を截って、我こそ産業戦士になりと堂々と闊歩してもらいたいためなのである。かくする者に必要と思われる胸中の一端を披瀝する』
と前提して朝鮮統治の方針を今日に至るまでの朝鮮統治の経緯を述べる総督の一句一句は入所式をいまさきに終えたばかりの学徒の気持を静かに落ち着かせ、先ず昨年末頃から半島に殉国の精神が澎湃として興った点を指摘。今日まで半島における総督政治を妨げたものに支那思想、米英思想、最後に共産主義があると述べ、『支那思想は高麗時代の腐敗した仏教に代るに李朝が儒教を主教とし支那の総ての思想に心酔した余りに日本の政治を妨害した。次が米英思想としてキリスト教があり、これは英米自己流の論理道徳を押しつけんとするに過ぎないものであって、その裏には搾取の野望が蔵されており、日本の一視同仁を快からず思った。これにつぐものに共産主義あり』と講述。
ここで朝鮮人の本質は内地の一部、満州、北支で非難されているが如きものでなく、この非難は李朝五百年に醸し出された今日よかれの生活が然らしめたと断定。朝鮮の本質こそは遠く朝鮮民族の根源に溯って探求され、この根源は日本書紀の中に求められると明確に指摘。内鮮同祖同根論が力強い論旨をもって熱心に耳を傾ける学徒の前に繰展げられた。
『これに反対するものがあれば日本書紀に明々白々に書いていることに反対することになる。朝鮮民族の本質を洗ってみるに内鮮同祖同根は明確である。今日内鮮一体と言わざるを得なかったのに之が究明の足らざるところがあった。我々は内鮮の持ち来った文化、国体の本義を把握する必要があると考える。然らば我々の祖先は如何なる精神文化体系を持っているかを考えねばならない。国体の本義を把握するのに我々の記憶せねばならないことは国体明徴、斎鏡斎穂、神鏡盤境の三神勅である』
総督は次々と三神勅の深淵なる哲理を判り易く説明。聴く学徒は今は澄んだ心境に一句一句を彫みこむのであった。更に語を継いで八神殿の哲理に含まれている精神を説き三神勅を究めることをすすめ、『之を究め尽くした時諸君の精神にはびこる李朝五百年の儒教が流した害毒を払拭出来る』と優しく悟し、
『このことをもう少し早くしんみりと語明すことが出来たとすれば諸子を今日よりもって幸福な境地に進ませたと思う』と語る総督はこのこと故前夜も、その前夜も夜遅くまで長時間に亘って先ず教育に携わっている者に対し、既に神代に織り成した偉大なる精神文化の体系に国体の本義を究め、道義朝鮮の確立を絶叫して来たのである。最後に、『今迄のことは水に流し世に処し、男と生れた以上、精神の理念を明かに把握せなばならない。酔生無死せばこの世に存在の意義はない。生存の意義は国体の本義に透徹することにあり、この雄大なる哲理を残した祖先に合一してゆくことにある』と述べ、『時機があれば諸君が在訓練中にもう一度訪れ諸子に接したい。諸子に期待している念願は判ったと思うが、判ったかね』と双頬を綻ばせて質せば応徴学徒は”ハイッ”と力をこめてこれに応えた。
かくして二時間に亘る訓話を終えた総督は同訓練所で夕食を摂り同六時過ぎ帰路についた。
Source: 키워드 검색 – 신문 검색 – 대한민국 신문 아카이브