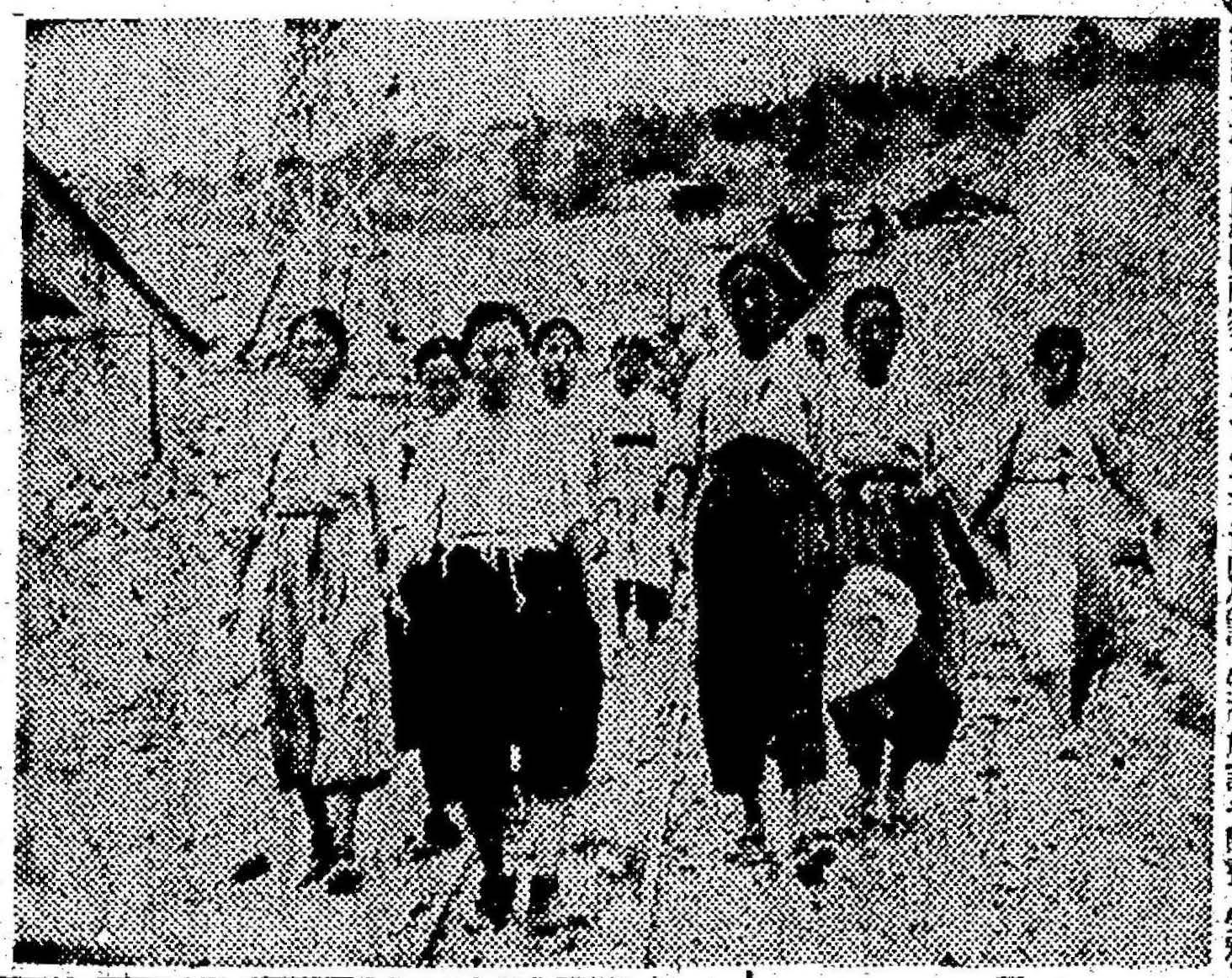Koreans faced up to 10 years in prison and 50,000 yen in fines for not submitting their personal platinum items to the Imperial Navy by Jan. 31, 1945
2025-01-06
159
1297
In the closing months of 1944, the Imperial Japanese Navy escalated its efforts to extract resources from Korea to fuel its war machinery. Initially, they encouraged Koreans to donate or sell their platinum items to support the production of warplanes. However, as the war situation became more desperate, the messaging shifted from voluntary contributions to mandatory requisitions backed by severe penalties, as evidenced in the following December 29, 1944 article from Keijo Nippo, the propaganda newspaper of the Imperial Japanese colonial regime which ruled Korea at the time.
The government offered compensation of 90 yen for 1 monme (approximately 3.75 grams) of platinum, which would be roughly $2,000 USD in today’s money. Yet, this apparent generosity is questionable. In the same breath, the article threatens up to 10 years of imprisonment and fines up to 50,000 yen (close to one million USD today) for anyone who fails to comply by the January 31, 1945 deadline. Such exorbitant fines cast doubt on whether the promised compensation was ever genuinely intended.
This stark shift contrasts sharply with previous campaigns, like the 1943 brass donation drive, where the emphasis was on selfless contribution without expectation of compensation. The propaganda newspaper Keijo Nippo were replete with stories glorifying private donations, embodying the spirit of sacrifice expected from all citizens in Korea at the time.
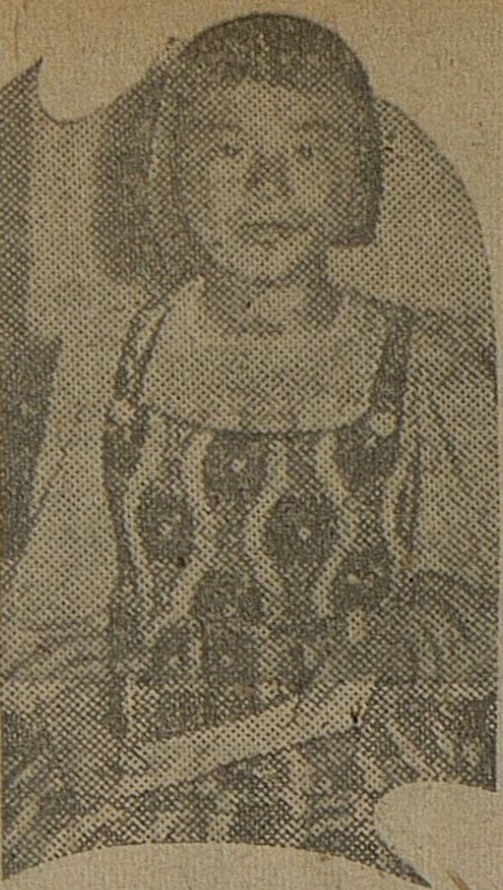
A poignant example is the October 13, 1944 article about 13-year-old Yūko Yamagishi, who innocently donates her mother’s platinum diamond ring to the Imperial Navy. Portrayed endearingly, her actions were meant to model the ideal behavior the colonial regime sought from Koreans: to give freely to the military without expecting anything in return.
This tactic of using children in propaganda was a recurring theme in Imperial Japanese media. By highlighting such stories, the regime aimed to tug at the heartstrings of the populace, fostering a culture of unquestioning support and sacrifice to help Japan in its war against the US and Britain during WWII.
[Translation]
Gyeongseong Ilbo (Keijo Nippo) October 13, 1944
She found the “Ring to Destroy the Enemy”!
“Please use it quickly,” she said eagerly, as she donated it
A child’s pure patriotism offering platinum
“One gram of platinum can sink an enemy battleship.” This priceless resource was being mobilized entirely, without leaving a single speck behind, to destroy the ever-approaching enemy forces growing arrogant in their numbers. The platinum contribution campaign has accelerated, reaching the point of mandatory buybacks. However, there was one girl who provided a major impetus to those who were reluctant to part with their “last precious items” or dismissing their own contributions as “too small.” She demonstrated her sincerity in supporting the production of spirit-imbued weaponry by offering up without hesitation a platinum diamond ring (worth 200 yen) that she had kept in a safe place. Stirred with a youthful fighting spirit, she reasoned, “If platinum is so essential for increasing aircraft production, I’m going to donate it instead of selling it!“
This patriotic young girl lived in Takezoe-chō (present-day Chungjeong-no), Seodaemun District, Seoul. Her name was Yūko Yamagishi (13 years old), the eldest daughter of Sadayoshi Yamagishi. She is currently a sixth-grader at Seodaemun Elementary School. Every time Yūko read the newspaper, she learned how crucial platinum was and how indispensable it was for increasing aircraft production. She thought, “Isn’t there more platinum out there? Why won’t the people who have platinum not offer it up sooner?” Then, she remembered that she had safely kept a small, beautiful platinum ring with a diamond that her mother had given her, saying, “You can wear this when you grow up.“
Unable to remain still any longer, Yūko searched through the drawers of her cabinet, found the ring, and excitedly consulted her mother, Taka, saying, “Please let me donate this instead of selling it.” Taka was deeply moved by her daughter’s noble feelings and encouraged her, saying, “Thank you for saying that. Please donate it with your own hands.“
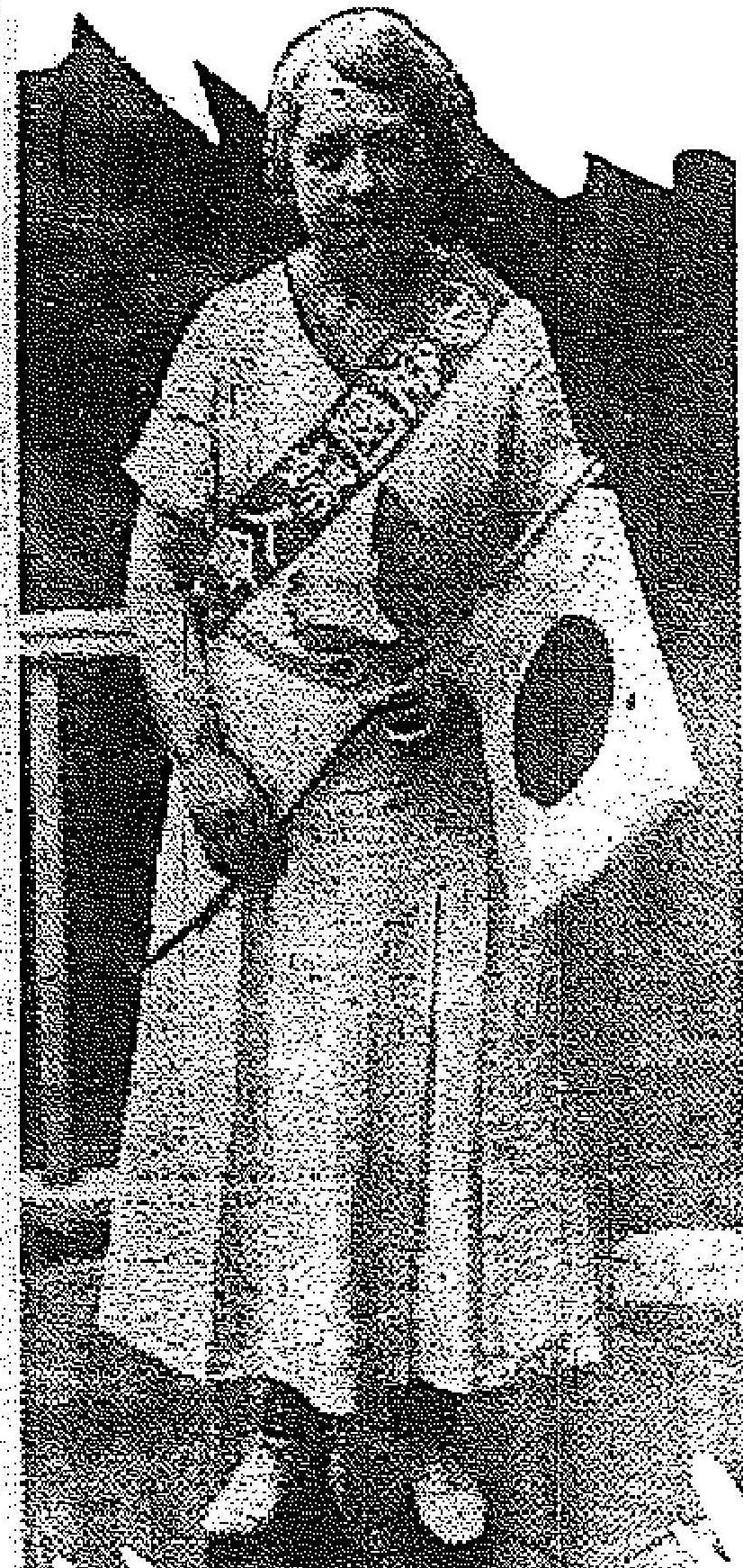
Yūko wrote a letter of donation addressed to Colonel Matsumoto of the Naval Military Office, saying, “This ring may be small, but please accept it along with my heartfelt sincerity.” She visited the head office of this newspaper on the 12th and entrusted her ring to the donation desk. [Photo: Yūko donating her platinum]
**Yūko’s Letter to Colonel Matsumoto (unedited)**
Dear Colonel Matsumoto,
Through newspapers, I have learned that the decisive battle in the air, which will determine the fate of the Imperial Nation, is fast approaching. I also understood how important platinum is for increasing aircraft production. Then, I remembered the platinum diamond ring that my mother had given me. She told me, “Wear this when you grow up.”
When I think of Tarawa, Makin, and Saipan Island, I can no longer remain idle. I want to donate this ring as quickly as possible to help in any way I can. When I told my mother about this, she wholeheartedly agreed. I wanted to bring it immediately, but I needed to go to school next Sunday, so I couldn’t go myself. Instead, I have asked this one man that I know to deliver it on my behalf.
Please use this precious ring, which I have cherished, to build as many fine aircraft as possible and defeat the hated British and Americans. I earnestly pray for your success.
Banzai to the Japanese Air Force!
Sincerely,
Yūko Yamagishi,
Sixth-grader at Seodaemun Public School, Seoul
**Statement from Yūko’s mother Taka**
“I brought this ring with me when I got married, but I gave it to my daughter when she said that she wanted it, and I had forgotten about it. Yesterday, she created a great fuss, rummaging through her desk and drawers, and when she finally found the ring, she shouted ‘Platinum, platinum!’ with joy. When I asked her what she was doing, she replied, ‘I am going to donate this to make airplanes!’ That was when I understood her intentions and felt overjoyed. Though it is such a small item, I hope my daughter’s sentiments will contribute to the creation of great weaponry.”
Gyeongseong Ilbo (Keijo Nippo) December 29, 1944
Platinum: Now Subject to Mandatory Purchase
Refusal May Lead to Imprisonment of Up to Ten Years
The voluntary purchase of platinum by the Navy Purchasing Agency and the Material Management Agency concluded successfully on November 30. However, in response to the current war situation, a new Governor-General’s ordinance issued on December 5 mandates the compulsory acquisition of platinum. The important Material Management Agency has been designated as the purchasing authority to enforce this measure. We request that platinum submission be made through the Seoul city government, the Korean Federation of National Power (Seoul Branch), Patriotic Women’s Association (Seoul Branch), and the Material Management Agency.
The platinum subject to compulsory acquisition includes privately owned platinum and platinum alloys, such as jewelry, ornaments, personal accessories, stationery, fixtures, or even scrap materials. Exceptions apply to items classified as national treasures or those personally granted by the Emperor, provided the recipient has obtained permission from the Governor to retain them.
The procedure for submission requires individuals to fill out appropriate forms or postcards with their address, name, item descriptions, and quantities, and send them to the Material Management Agency. Alternatively, collective submissions through patriotic groups, labor unions, or other organizations are permitted.
The acquisition period ends on January 31. Applications and submission of items must be completed by this date, except for certain items requiring substitutes. The standard price is set at 90 yen per monme (3.75 grams), while government-owned items are priced at 61 yen, 2 sen, and 5 rin.
Severe penalties are imposed for violations, including reselling or deliberately destroying platinum products, failing to submit an application by January 31, or refusing requests for collection by the agency. Such actions may result in imprisonment of up to ten years or a fine of up to 50,000 yen.
[Transcription]
京城日報 1944年10月13日
あった”撃敵の指輪”
早く使って下さいと勇んで献納
白金を捧ぐ幼きこの赤心
”白金一匁はよく敵戦艦を撃沈する”この尊い百金を一粒残さず根こそぎ動員し、量に驕りじりじりと迫って来る敵を撃滅しようと白金供出運動は一段と拍車を加え今や強制買上げとなったが、飛行機増産になくてはならぬ白金ならば売るよりも献納しましょうと幼い闘魂を沸かせて大切に仕舞ってあった白金ダイヤ入り指輪(二百円)を惜しげもなく捧げ魂のこもる兵器の増産に赤誠を示し”これだけは”とか”こんな小さな物は”と出し渋っている人達に大きな刺戟を与えた軍国少女がある。
京城府西大門区竹添町三丁目山岸貞良氏長女裕子さん(13)=西大門国民校六年=は新聞を読む度毎に白金が如何に重要であり、飛行機の増産になくてはならないということを知り、”白金は無いものだろうか、どうして持っている人達が早く出さないのだろうか”と考えているうちに何時かお母さんから大きくなったら使いなさいと戴いた小さな可愛いダイヤ入り白金の指輪を大切に仕舞っておいたことに気が付いた。もうじっとしていられなくなった裕子さんは箪笥の中から探し出し喜び勇んで売るよりも献納させて下さいと母親たかさんに相談した處、たかさんも娘の麗しい気持ちに胸が一ぱいとなり”よく言って呉れました、あなたの手で献納して下さい”と激励した。裕子さんは指輪は小さいが私の真心とともに是非受け取って下さいと海軍武官府松本大佐宛に献納文を綴り、これを添えて十二日本社を訪れ献納方寄託した。【写真=白金献納の裕子さん】
(原文のまま)松本大佐さま、私は新聞で皇国の興廃がきまる航空決戦が間近かに迫り、飛行機増産の為に白金がどんなに大切であるかを知りました。そして私が大きくなった時お使いなさいといってお母さまからいただいた白金にダイヤのはいった指輪のあることに気がつきました。タラワ、マキン、サイパン島のことを思うとき私はもうじっとしていられません。一刻も早くこの指輪を献納してお役に立てたいと思ってそのことをお母さまに話すとお母さまも大賛成でした。早速持って行こうと思いましたが今度の日曜も学校があるので行けません。それで知り合いのおじちゃんに頼んでお届けします。どうか私が大切にしていたこの指輪でりっぱな飛行機を少しでもたくさん造って憎い米英をやっつけて下さい。お願いいたします。日本航空部隊バンザイ...京城府西大門国民学校六年生山岸裕子
母親たかさんは語る:”私が嫁入りするとき持って来ましたのですが、娘が欲しいというのでやってしまい忘れていました。それが昨日ですが一人でえらい騒ぎをしながら机や箪笥の中をひっかきまわし指環を探し出し”白金、白金”と大きな声で喜ぶのでどうしたのかと聞きますと、”これを献納して飛行機を造りましょう”と言うのではじめて判り嬉しく思いました。こんな小さなものですが娘の心が通じて立派な兵器に役立って戴ければと思っています。
京城日報 1944年12月29日
白金:今度は強制買上げ
拒絶すれば懲役十年以下
白金買上げは海軍武官府指定買上班と物資営団で任意買上げを行い、好成績に十一月三十日一応終了したが、更に現戦局に応じ五日附総督府令で白金の強制買上げを断行することになったので重要物資営団が買上げ機関となり買上げを強行することに決定。京城府、同聯盟、日婦京城支部、物資営団で供出を要望している。
強制買上の白金は業者の手持品を含む民間所有の白金若しくは白金合金を使用した装飾品、装身具、身辺品、文房具、什器又は其の屑等であるが国宝物又は御下賜品拝受者が特にその所持を希望し同知事の許可を受けたものは供出しなくてもよい。
供出の方法は適宜の用紙、郵便はがき等で住所氏名、型、個数を記入し営団に宛譲渡の申込をするか都合により愛国班、組合その他の団体で一括申込も差支えない。
買上げ期間は一月末日までに申込み現品も代替物を要する特別のもの以外は同日迄に供出する。価格は普通一匁九十円、官有物は六十一円二銭五厘である。
白金製品を転売したり故意に滅失したり一月末日迄に譲渡の申込をせぬ場合又は営団の引取り請求を拒絶した場合は十年以下の懲役又は五万円以下の罰金に処せられる。
Source: National Library of Korea Digital Archive